Choosing the right type of dentures is a critical step in restoring oral functionality and aesthetics after tooth loss. While there are several types of dentures available today, metal dentures and plastic dentures stand out as two of the most commonly prescribed varieties. Each offers distinct benefits and limitations, and understanding their differences is vital for patients making informed decisions about their dental health.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, clinical applications, maintenance, and cost considerations of metal dentures versus plastic dentures. Our aim is to help patients, caregivers, and dental professionals make evidence-based choices tailored to individual needs.
Understanding Dentures
Dentures are removable prosthetic devices designed to replace missing teeth and the surrounding tissues. They come in various forms, such as complete dentures (for patients missing all teeth) and partial dentures (for those who have some natural teeth remaining). Dentures not only restore functionality but also improve appearance and prevent the facial sagging that often accompanies tooth loss.
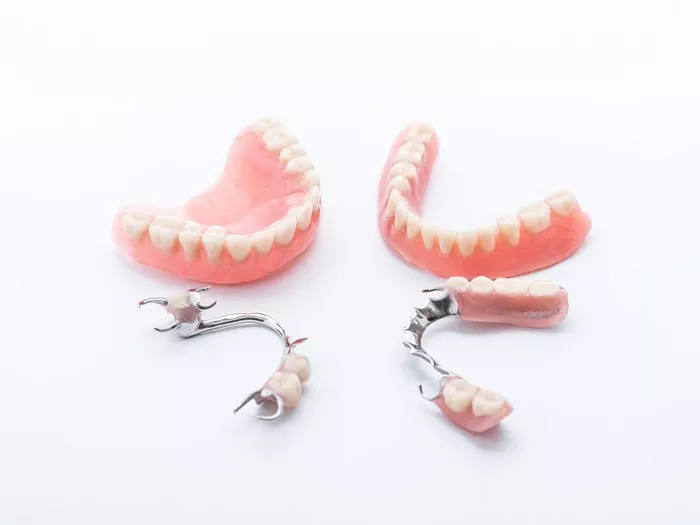
There are multiple materials used in the fabrication of dentures. Among them, metal and acrylic resin (plastic) are the most prevalent. While metal-based dentures typically consist of a cast metal framework (often cobalt-chrome), plastic dentures are usually made from polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), a type of durable acrylic.
Overview of Metal Dentures
Composition and Structure
Metal dentures are typically made using cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr) alloys, although titanium and stainless steel may also be used in specific cases. These dentures consist of a rigid metal framework that provides strength and stability. The teeth and gum-colored portions are embedded in an acrylic base that attaches to the metal frame.
Key Features of Metal Dentures
Lightweight yet strong: Despite their metallic composition, these dentures are lighter than one might expect due to the thinness of the alloy used.
Durable: Metal dentures are resistant to fracture and wear, offering long-term functionality.
Precise fit: These are typically custom-made using detailed impressions and CAD/CAM technology, ensuring better retention and comfort.
Less bulky: Metal frameworks allow for thinner designs compared to plastic dentures.
Overview of Plastic Dentures
Composition and Structure
Plastic dentures are made entirely of high-impact acrylic resin, typically polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). These are usually more affordable and quicker to fabricate. The entire structure, including the base and the artificial teeth, is formed from acrylic.
Key Features of Plastic Dentures
More flexible: Though not as strong as metal, plastic materials can offer some flexibility and are more forgiving to minor adjustments.
Easier to modify: Repairs and relines are simpler with plastic dentures.
Suitable for temporary or immediate use: Plastic dentures are often used as transitional or immediate dentures following tooth extraction.
Lower initial cost: Fabrication is simpler and generally less expensive than metal dentures.
Metal Dentures vs Plastic Dentures
To better understand the suitability of each denture type, let’s compare metal dentures and plastic dentures across several important categories:
1. Aesthetics
Metal Dentures: The metal framework is usually hidden behind the teeth and gums, making it discreet. However, in some cases, the clasps used to retain the denture may be visible, especially in the anterior region.
Plastic Dentures: Since they are made entirely from gum-colored acrylic, plastic dentures often appear more natural in the mouth. This can be an aesthetic advantage, particularly when visibility is a concern.
Verdict: Plastic dentures may offer a slight edge in visible aesthetics, though both types can be made to look natural with skilled craftsmanship.
2. Comfort and Fit
Metal Dentures: Offer superior fit due to their rigidity and precision during fabrication. They are lighter and less bulky, which often improves speech and comfort.
Plastic Dentures: Can feel bulkier and heavier, especially in the upper jaw. Their softer nature can lead to minor discomfort over time, particularly with larger spans.
Verdict: Metal dentures generally provide a more comfortable, secure fit due to their structural advantages.
3. Strength and Durability
Metal Dentures: Highly durable and resistant to breakage or distortion. Ideal for long-term wear.
Plastic Dentures: More prone to cracks and wear, especially if dropped. The acrylic base can become brittle over time.
Verdict: Metal dentures are significantly more durable than plastic alternatives, making them more suitable for long-term use.
4. Oral Hygiene and Biocompatibility
Metal Dentures: Cobalt-chromium alloys are biocompatible, though metal may accumulate plaque if not cleaned properly. Their non-porous nature resists bacterial colonization better than plastic.
Plastic Dentures: Acrylic is slightly porous and can harbor bacteria if not cleaned thoroughly. Staining is more common.
Verdict: Both types require regular cleaning, but metal dentures may offer slightly better resistance to microbial buildup.
5. Adjustability and Repairs
Metal Dentures: Adjustments require specialized tools and expertise. Repairs are possible but more complex.
Plastic Dentures: Easy to adjust and repair. Chairside relines and modifications are simpler and more cost-effective.
Verdict: Plastic dentures are easier and quicker to modify or repair.
6. Cost
Metal Dentures: More expensive due to material cost, lab work, and time-consuming fabrication processes.
Plastic Dentures: More affordable, making them a popular choice for patients on a budget or needing immediate prostheses.
Verdict: Plastic dentures are more economical, particularly for short-term or transitional use.
7. Longevity
Metal Dentures: With proper care, they can last 10–15 years or more.
Plastic Dentures: Tend to last around 5–7 years, depending on wear and maintenance.
Verdict: Metal dentures are a better investment for patients seeking long-term solutions.
Clinical Indications for Each Type
When Metal Dentures Are Preferred
Patients with strong chewing forces or bruxism
Long-term partial denture needs
High expectations for fit, stability, and comfort
Minimal aesthetic concerns about visible clasps
When Plastic Dentures Are Recommended
Temporary or immediate dentures after extraction
Patients with limited financial resources
Rapidly changing oral conditions (e.g., after surgery or bone remodeling)
Interim solution before implants or fixed prosthetics
Patient Considerations: Factors Influencing the Choice
Patients should consider the following before choosing between metal dentures and plastic dentures:
1. Oral Health Status
Patients with healthy gums and minimal bone loss are ideal candidates for either type. Those with significant bone resorption may benefit from the thinner design of metal dentures.
2. Lifestyle and Habits
Patients who lead active lifestyles or have strong masticatory forces should consider metal dentures for their strength and resistance to breakage.
3. Budget
While metal dentures cost more initially, they offer better longevity. However, for patients with financial constraints, plastic dentures remain a viable alternative.
4. Future Plans
Patients planning for future implants or bridges may opt for plastic dentures in the interim.
5. Sensitivities or Allergies
Though rare, some individuals may have allergic reactions to certain metals. In such cases, titanium or plastic dentures may be preferable.
Maintenance and Care
Regardless of the type chosen, dentures require daily care and maintenance to ensure longevity and oral health.
For Metal Dentures:
Clean daily with a soft toothbrush and non-abrasive denture cleaner.
Avoid bleach-based cleaners that can corrode the metal.
Store in water when not in use to prevent drying and warping of the acrylic parts.
Schedule regular dental check-ups for adjustments.
For Plastic Dentures:
Use a denture brush and mild cleanser to remove debris.
Avoid hot water, which can deform the acrylic.
Soak in appropriate cleaning solution overnight.
Be cautious when handling to prevent accidental drops and fractures.
Prosthodontist’s Perspective
From a clinical standpoint, metal dentures are often preferred for their durability, precision, and comfort, particularly in long-term partial denture applications. However, plastic dentures serve a crucial role, especially when immediate or cost-sensitive solutions are required.
A hybrid approach is also becoming more popular—where the base is metal, but highly aesthetic components (like gum-colored flanges) are made from advanced plastics to improve the overall look without sacrificing strength.
Conclusion
When weighing metal dentures vs plastic dentures, the right choice depends on individual patient needs, oral anatomy, lifestyle habits, and financial considerations.
Ultimately, a thorough consultation with a dental professional is essential. A prosthodontist can assess the oral condition, listen to the patient’s goals, and recommend a tailored solution. Whether choosing metal dentures for their strength or plastic dentures for their affordability and aesthetics, patients can rest assured that both options offer viable pathways to restoring oral health and quality of life.
Related topics: