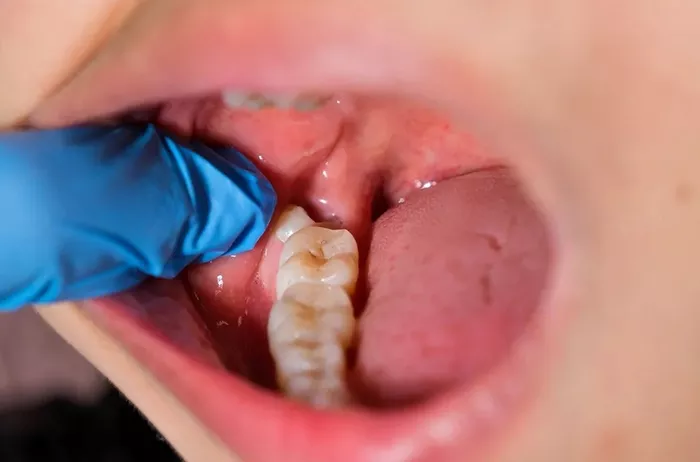
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, typically begin to emerge in the late teenage years or early twenties. While some individuals experience no complications with their wisdom teeth, others may encounter various symptoms indicating that their wisdom teeth are growing. Recognizing these signs early can help manage pain, prevent complications, and determine whether extraction is necessary.
Understanding the Basics of Wisdom Teeth
Wisdom teeth are the final set of molars located at the back of the mouth. Most people have four wisdom teeth—two on the top and two on the bottom. These teeth usually begin to push through the gums between the ages of 17 and 25. However, not everyone develops wisdom teeth, and some individuals may only have one to three.
Why Are Wisdom Teeth Problematic?
Unlike other teeth, wisdom teeth often have limited space to grow. As a result, they may become impacted or only partially erupt. This can lead to various dental issues and uncomfortable symptoms that require professional attention.
Common Symptoms of Growing Wisdom Teeth
Several symptoms may indicate that your wisdom teeth are starting to come in. The severity and type of symptoms vary from person to person, depending on factors such as the position of the teeth and the individual’s oral health.
1. Jaw Pain and Discomfort
One of the earliest and most common symptoms is jaw pain or discomfort. This often occurs in the back of the mouth where the wisdom teeth are trying to emerge. The pressure from the erupting teeth against existing molars can cause persistent aches.
2. Swollen or Tender Gums
As wisdom teeth break through the gum tissue, the area may become red, swollen, or tender to the touch. This inflammation can lead to sensitivity when brushing or eating. In some cases, a flap of gum called an operculum may partially cover the tooth, leading to additional irritation.
3. Difficulty Opening the Mouth
Limited jaw movement or difficulty opening the mouth is another symptom. This condition, called trismus, results from inflammation and muscle strain in the jaw area as wisdom teeth exert pressure on the surrounding tissues.
4. Headaches and Earaches
Wisdom teeth growth can sometimes lead to tension headaches or referred pain in the ears. Since the jaw and ear structures are closely connected, pressure or inflammation in one area can affect the other.
5. Bad Breath and Unpleasant Taste
When wisdom teeth partially erupt, it becomes difficult to clean the area properly. Food particles and bacteria can get trapped, leading to bad breath and a foul taste in the mouth.
6. Cysts or Infections
In more severe cases, a fluid-filled sac or cyst can form around an impacted wisdom tooth. These cysts can damage surrounding teeth and bone. If left untreated, infections such as pericoronitis may develop, causing more intense symptoms.
Less Common But Serious Symptoms
1. Shifting Teeth and Bite Changes
As wisdom teeth push against adjacent molars, they may cause tooth crowding or shifts in alignment. This can alter your bite and potentially reverse the effects of previous orthodontic work.
2. Swollen Lymph Nodes
In some cases, an infection related to wisdom teeth can lead to swollen lymph nodes in the neck or under the jaw. This indicates that your body is fighting off infection and may require antibiotics or other treatment.
3. Fever and General Malaise
When an infection spreads beyond the mouth, it can trigger systemic symptoms like fever, fatigue, and a general feeling of being unwell. These are warning signs that should not be ignored.
Identifying Impacted Wisdom Teeth
Impacted wisdom teeth do not have enough space to emerge or develop normally. There are several types of impactions, and each may cause different symptoms:
1. Vertical Impaction
The tooth is angled upright but fails to fully erupt through the gum line.
2. Mesial Impaction
This is the most common type and occurs when the tooth is angled forward toward the front of the mouth.
3. Distal Impaction
The tooth is angled backward toward the rear of the mouth, which is less common.
4. Horizontal Impaction
The tooth lies completely on its side, often pressing against the roots of neighboring teeth and causing intense pressure and pain.
How to Diagnose Growing Wisdom Teeth
1. Clinical Examination
A dentist will begin with a visual examination of the mouth to assess gum condition, swelling, and visible signs of tooth eruption.
2. Dental X-Rays
X-rays are essential in diagnosing the position of wisdom teeth and determining whether they are impacted or likely to cause complications. Panoramic or periapical X-rays provide comprehensive views of the jaw.
Home Remedies for Temporary Relief
While waiting for a dental appointment, certain home remedies can offer temporary relief from symptoms:
1. Saltwater Rinse
Rinsing with warm salt water can help reduce inflammation and clear bacteria from the affected area.
2. Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress to the outside of the cheek can help numb pain and reduce swelling.
3. Over-the-Counter Pain Medications
Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide temporary relief from pain and discomfort. However, these medications do not treat the underlying cause.
When to See a Dentist
If symptoms persist or worsen over time, it’s crucial to see a dentist. Professional evaluation is necessary if you experience:
- Severe pain that disrupts daily activities
- Swelling that doesn’t subside after a few days
- Signs of infection like fever or pus
- Difficulty chewing or opening the mouth
Possible Treatments for Wisdom Teeth Symptoms
1. Monitoring Growth
If the teeth are erupting normally without causing issues, the dentist may recommend monitoring the growth periodically with check-ups and X-rays.
2. Antibiotics
If an infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to manage bacterial growth before any surgical intervention.
3. Wisdom Teeth Extraction
Surgical removal is often recommended for impacted or problematic wisdom teeth. The procedure is usually performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on complexity and patient preference.
Preventing Wisdom Teeth Complications
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Regular brushing and flossing can prevent infections and bacterial buildup around erupting teeth.
2. Attend Regular Dental Check-Ups
Routine dental visits help monitor wisdom teeth development and allow early intervention if problems arise.
3. Early Screening
Dental professionals may recommend evaluating wisdom teeth with X-rays in the mid-teen years to anticipate and plan for future growth.
FAQs About Growing Wisdom Teeth
Q1: Do all people get wisdom teeth?
No, some individuals never develop wisdom teeth, while others may have fewer than four. Genetics play a significant role in this variation.
Q2: Can wisdom teeth grow without causing pain?
Yes, some people experience little to no discomfort during wisdom teeth eruption. However, monitoring is still important to ensure proper growth.
Q3: What age do wisdom teeth usually appear?
Wisdom teeth typically begin to emerge between the ages of 17 and 25. However, they can erupt earlier or later in some cases.
Q4: Is it necessary to remove all wisdom teeth?
No, removal is only necessary if the teeth are impacted, misaligned, or causing symptoms. A dentist will determine the best course of action based on individual assessment.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of growing wisdom teeth is essential for maintaining oral health and avoiding complications. Common signs include jaw pain, gum swelling, limited mouth opening, and bad breath. While some individuals may not experience severe discomfort, others may require intervention, including extraction. If you suspect your wisdom teeth are emerging, consult a dental professional for evaluation and guidance. Early detection and treatment can prevent long-term issues and ensure a smoother dental experience.
Related topics